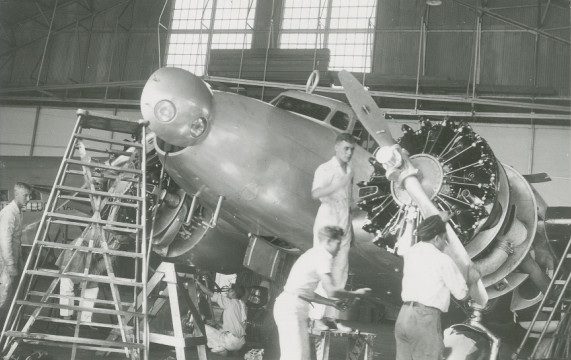
The Corsair was designed by Rex Buren Beisel, and is best known for its distinctive inverted “gull wing,” which allowed sufficient ground clearance for its 13 foot, 4 inch (4.064 meter) diameter propeller, without using excessively long landing gear struts. The prototype XF4U-1, Bu. No. 1443, had first flown 29 May 1940, with test pilot Lyman A. Bullard in the cockpit.
The F4U-1 was had a length of 33 feet, 4.125 inches (10.163 meters), wingspan of 40 feet, 11.726 inches (12.490 meters) and overall height (to top of propeller arc) of 15 feet, 0.21 inches (4.577 meters). The wings’ angle of incidence was 2°. The outer wing had 8.5° dihedral and the leading edges were swept back 4°10′. With its wings folded, the width of the F4U-1 was 17 feet, 0.61 inches (5.197 meters), and gave it a maximum height of 16 feet, 2.3 inches (4.935 meters). When parked, the Corsair’s 13 foot, 4 inch (4.064 meter) propeller had 2 feet, 1.93 inches (65.862 centimeters) ground clearance, but with the fighter’s thrust line level, this decreased to just 9.1 inches (23.1 centimeters). The F4U-1 had an empty weight of 8,982 pounds (4,074.2 kilograms) and gross weight of 12,162 pounds (5,516.6 kilograms).



The F4U-1 had a cruise speed of 186 miles per hour (299 kilometers per hour) at Sea Level. Its maximum speed at Sea Level was 365 miles per hour (587 kilometers per hour). During flight testing, an F4U-1 reached 431 miles per hour (694 kilometers per hour) at 20,300 feet (6,187 meters) with War Emergency Power. The service ceiling was 38,200 feet (11,643 meters) and its maximum range was 1,510 miles (2,430 kilometers) with full main and outer wing tanks.
The Corsair was armed with six air-cooled Browning AN-M2 .50-caliber machine guns, three in each wing, with 400 rounds of ammunition per gun.

A total of 12,571 Corsairs were manufactured by the Vought-Sikorsky Aircraft Division (F4U-1), Goodyear Aircraft Corporation (FG-1D) and Brewster Aeronautical Corporation (F3A-1). The Corsair served the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps in World War II and the Korean War. Corsairs also served in other countries’ armed forces. Its last known use in combat was in Central America in 1969.

© 2019, Bryan R. Swopes