24 June 1939: The Pan American Airways System began scheduled air service from the United States to Britain. The Boeing 314 Yankee Clipper, NC18603, made the first flight from Port Washington, New York, departing at 8:21 a.m. It made intermediate stops at Shediac, New Brunswick, and Botwood, Newfoundland, where fog delayed the flying boat until 12:49 p.m., 28 June. Continuing across the Atlantic, Yankee Clipper made another stop at Foynes, Ireland, and finally arrived at Southampton at 7:25 p.m. that evening.
24 June 1939: The Pan American Airways System began scheduled air service from the United States to Britain. The Boeing 314 Yankee Clipper, NC18603, made the first flight from Port Washington, New York, departing at 8:21 a.m. It made intermediate stops at Shediac, New Brunswick, and Botwood, Newfoundland, where fog delayed the flying boat until 12:49 p.m., 28 June. Continuing across the Atlantic, Yankee Clipper made another stop at Foynes, Ireland, and finally arrived at Southampton at 7:25 p.m. that evening.
The largest airplane of the time, the Pan American Clipper flying boat could carry 77 passengers in “one class” luxury, with a ticket priced at $675—that’s in 1939 dollars. ($12,389.82 in 2020) Uniformed waiters served five and six course meals on silver service. Seats could be folded down into beds.

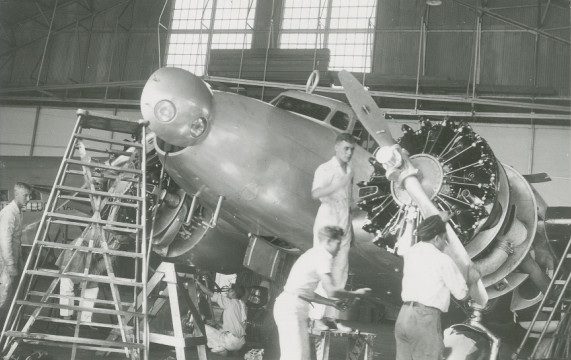
 The Boeing Model 314 was a large four-engine, high-wing monoplane flying boat designed and built by the Boeing Airplane Company to take off and land on water. It had a crew of 10. The wings and engine nacelles had been designed for Boeing XB-15 heavy bomber. It was 106 feet (32.309 meters) long with a wingspan of 152 feet (46.330 meters). It had a maximum take off weight of 82,500 pounds (37,421 kilograms).
The Boeing Model 314 was a large four-engine, high-wing monoplane flying boat designed and built by the Boeing Airplane Company to take off and land on water. It had a crew of 10. The wings and engine nacelles had been designed for Boeing XB-15 heavy bomber. It was 106 feet (32.309 meters) long with a wingspan of 152 feet (46.330 meters). It had a maximum take off weight of 82,500 pounds (37,421 kilograms).
The Boeing 314 was powered by four air-cooled, supercharged, 2,603.737-cubic-inch-displacement (42.668 liter) Wright Aeronautical Division Cyclone 14 GR2600A2, two-row, 14-cylinder radial engines with a compression ratio of 7.1:1. They were rated at 1,200 horsepower at 2,100 r.p.m., and 1,550 horsepower at 2,400 r.p.m. for takeoff, burning 91/96 octane gasoline. These engines (also commonly called “Twin Cyclone”) drove three-bladed Hamilton Standard Hydromatic full-feathering constant-speed propellers with a diameter of 14 feet (4.267 meters) through a 16:9 gear reduction. The GR2600A2 was 5 feet, 2.06 inches (1.576 meters) long and 4 feet, 7 inches (1.387 meters) in diameter. It weighed 1,935 pounds (878 kilograms). The engines could be serviced in flight, with access through the wings.

The Boeing 314 had a maximum speed of 199 miles per hour (320 kilometers per hour), with a range of 3,685 miles (5,930 kilometers) at its normal cruising speed of 183 miles per hour (295 kilometers per hour). Its service ceiling was 13,400 feet (4,084 meters). The fuel capacity was 4,246 gallons (16,073 liters).
Boeing built six Model 314 and another six 314A flying boats for Pan American Airways and British Overseas Airways Corporation.
Yankee Clipper was destroyed 22 February 1943 at Lisbon, Portugal. A wing hit the water on landing. 24 of the 39 persons aboard were killed.

© 2017, Bryan R. Swopes